Preparing monomers for PySoftK
PySoftK is a code that enables the creation of polymers with different compositions and topologies delivering an equilibrated initial configuration. Initially, the user needs to prepare the monomer(s) by signalling the specific molecular regions where the bond creation will take place. Usually a place-holder (such as a predefined atom) can be used for this purpose.
To explicitly show the process, we will use a furan molecule. By using a common visualization program (such as VMD), the functionalization process is presented below
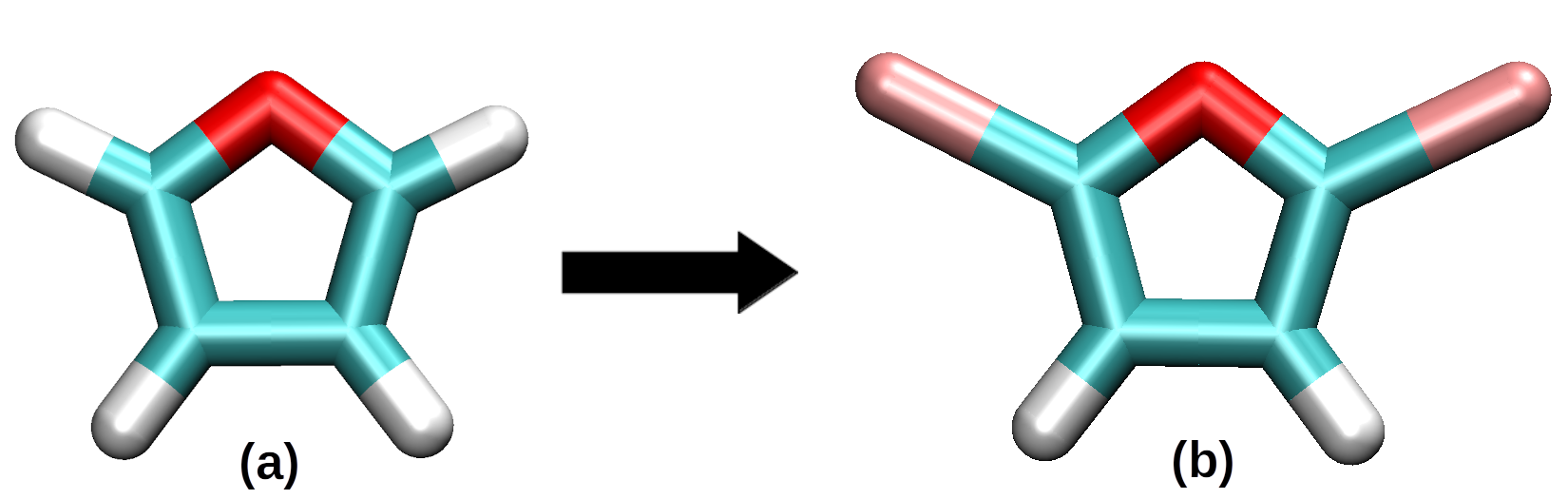
(a) Represents a furan molecule, while (b) represents a functionalized furan monomer in which two Bromine atoms are placed at the edges of the mioety and used as place-holders for the places in the monomer which will be bonded to neighboring monomers. The user can use any atom (PySoftK is agnostic to the used place-holder), as long as the same atom is used to indicate the regions of the molecule used to create a bond.
All the enabled RDKit formats are accepted as shown above:
from rdkit import Chem
from rdkit.Chem import AllChem
# SMILES FORMAT
mol_1=Chem.MolFromSmiles('c1(ccc(o1)Br)Br')
# MOL FORMAT
mol_2=Chem.MolFromMolFile('furan_pysoftk.mol')
#PDB FORMAT
mol_3=Chem.MolFromPDBFile('furan_pysoftk.pdb')
The defined molecules (mol_1, mol_2, and mol_3) demonstrate the various valid formats that can be used to input the structure of a monomer to PySoftK in order to create initial structures of a desired polymer.
Atomic Placeholders for PySoftK
As mentioned previously, PySoftK is agnostic to the use of any atomic place holders defined by the user. As an example, the molecule thiol has been functionalised with the atom Pt as can be seen in the following snippet:
from rdkit import Chem
from rdkit.Chem import AllChem
# SMILES FORMAT
mol_1=Chem.MolFromSmiles("c1(ccc(s1)[Pt])[Pt]")
This monomer can be further used to construct polymers as indicating in the following tutorials.